Welcome to an era where every text is a potential connection, and every relationship can lead to a possible long-term customer.

Monitoring SMS performance is crucial for maximizing ROI, engaging consumers, and preventing filtering or blocking by cell carriers.
Read on to learn why SMS delivery is important, common delivery issues, and how to resolve them.
Why is SMS delivery and reliability so important?
SMS delivery and reliability are essential for assessing the performance of marketing campaigns.
They confirm how many messages reached the intended recipients, helping you to evaluate content, timing, and frequency effectiveness.
Additionally, delivery reports help segment contacts based on responsiveness, allowing tailored follow-up messages or incentives.
If you want to learn more about Bulk SMS Marketing and how to ensure reliable SMS delivery, you can check out this comprehensive guide on Bulk SMS Marketing: The Definitive Guide.
The Significance of SMS Deliverability
Marketing effectiveness
SMS is undoubtedly still a powerful marketing channel due to its ability to reach a large percentage of your target audience, and delivery failure might result in missed marketing opportunities and revenue loss.
Compliance
SMS marketing is regulated by several rules and legislation, such as the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA) in the United States. Compliance often calls for verification of message delivery along with opt-in/opt-out approaches.
Customer engagement
SMS open rates are high, suggesting that most recipients read their SMS messages.
When messages don’t get through, engagement rates drop, which makes campaigns less successful. Reliable delivery ensures businesses can connect with their customers and keep their relationships strong.
Feedback and optimization
SMS delivery reports provide valuable information on how your campaign is performing. They help companies track bounce rates, response rates, and delivery quality. This data can help them make their SMS marketing better, improve content, and boost ROI.
Emergency communication
SMS is frequently used for emergency notifications such as disasters, public safety announcements, and health alerts. During a crisis, instant delivery remains vital for public safety, and message failures can have catastrophic consequences.
Brand reputation
Consistent and reliable SMS delivery helps to build a strong brand reputation. Customers who experience delivery issues or repeatedly get “failed to send” notifications may lose trust in the sender, damaging the brand’s image.
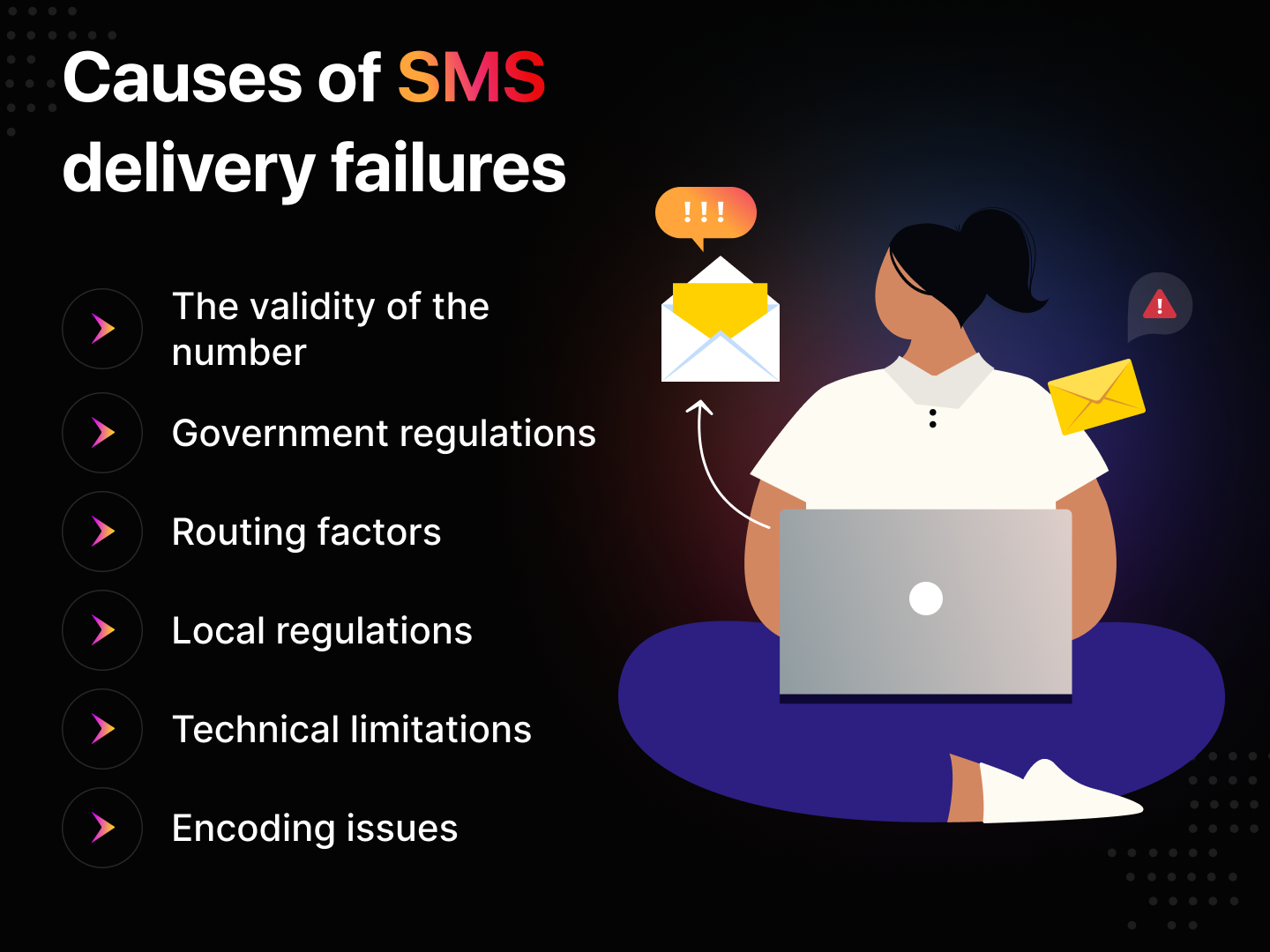
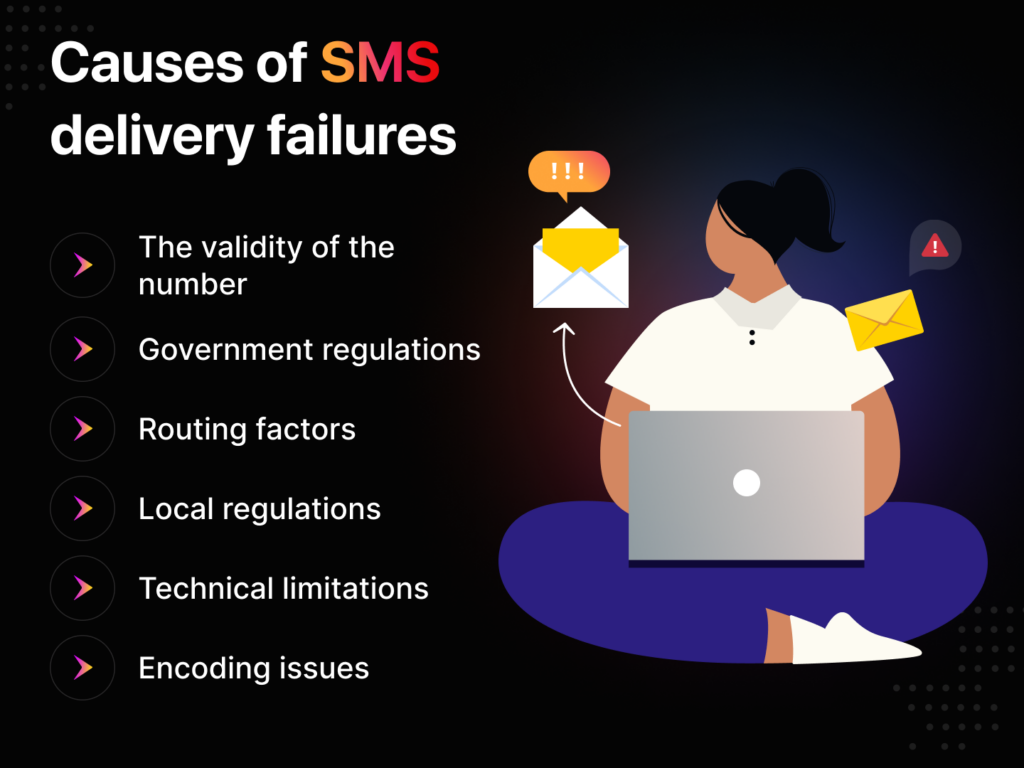
Common reasons for text messaging delivery failures
Achieving a 100% delivery rate in SMS campaigns is challenging.
And global messaging through A2P platforms or SMS APIs is a complex process with hidden elements you may not know about.
Here are some of the most common reasons SMS messages fail to reach their intended receivers.
Causes of SMS Delivery Failures
Carrier/content filters:
- Mobile operators use spam filters to block messages with sensitive content, such as political, religious, or sexual nature.
- Operators may block recurring messages sent through A2P routes, leaving out only P2P messages.
To minimize the impact of these filters, use valid and legal content, avoid sensitive words, and send messages through A2P-enabled routes.
The validity of the number:
- Messages may fail to deliver if the number is not valid or does not exist. Reasons for invalid numbers include missing international country codes, porting to a new network, using landline numbers, or incorrect phone numbers.
Government regulations:
- Different countries have rules that may block specific messages or sender IDs, such as the Do-not-Disturb feature.
Routing factors:
- Messages may be routed through networks not supporting message delivery, leading to failure. Using direct connections and ensuring correct routing can help improve delivery.
User out of reach:
- Mobile operators typically use a “store and forward” model, where messages are held for 48 to 72 hours. If the recipient’s device is unavailable during this time, the message may be discarded.
Local regulations:
- Some countries have specific rules, like time restrictions on message delivery, which can affect whether messages are delivered.
Technical limitations:
- Messages might not be delivered due to issues like full memory, coding errors, temporary disconnection from the network, or lack of support for certain message types or characters by the recipient’s phone.
Encoding issues:
- Local carriers may not support certain encodings, leading to message delivery problems.
Roaming:
- Users who are roaming may be harder to reach due to the design of telecommunication networks, potentially resulting in message delivery failures.
Troubleshooting Text Message Delivery Issues
To fix text messages not being delivered, you can consider the following steps and solutions based on the information provided:
Compliance
Make sure that your SMS campaigns follow local laws and industry standards. This includes obtaining proper authorization from recipients and offering opt-out choices. Noncompliance might result in delivery issues as well as legal implications.
Sender reputation
Send relevant and helpful SMS messages to maintain a positive reputation. Sending unsolicited or spammy information might damage your reputation and result in decreased deliverability rates.
Opt-in subscribers
Build your subscriber list with people who have specifically requested to receive SMS messages from your company, reducing the risk of SMS outbound failure by ensuring that users are engaged and interested.
Clean and up-to-date data
Clean up your contact list frequently, removing invalid or inactive phone numbers. Outdated or incorrect numbers can lead to failed deliveries. Use SMS service providers with systems in place for verifying and updating phone number databases.
Sender ID
Make your Sender ID more recognizable and trustworthy. Using a distinctive Sender ID improves the chances of your communications being delivered.
Mobile network connectivity
For greater deliverability across multiple locations, ensure your SMS service provider has reliable network operators.
To ensure seamless delivery across multiple locations, consider using our SMS API service for enhanced mobile network connectivity.
Delivery reports and monitoring
Regularly track and analyze delivery reports provided by your SMS carrier. These reports include information on delivery rates, failed deliveries, and other metrics that might assist you in optimizing your SMS campaigns.
Message content and formatting
Send SMS messages that are brief and clear while sticking to character limitations (often 160 characters). Using special characters or excessive abbreviations can result in message truncation or delivery issues.
Timing
To improve deliverability, consider timing your SMS messages. Avoid sending messages during late-night hours or when recipients are less likely to be available or receptive.
Testing and optimization
To improve deliverability rates, use A/B testing and experiment with alternative message formats, timing, and targeting. Optimize your SMS outbound marketing regularly, depending on data and feedback.
SMS Delivery Formula
SMS Delivery Rate = (Number of Messages Delivered / Total Number of Texts Sent) * 100%
This formula calculates the percentage of text messages sent successfully, typically called the SMS delivery rate.
To maintain a good delivery rate and assess the quality of your SMS database, it’s recommended to aim for a rate of around 98%.
Tracking and analyzing this rate, along with SMS delivery rates, across multiple periods (monthly, quarterly, and lifetime) is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of your SMS marketing plan.
Ways to Improve Your SMS and MMS Delivery Rate
Invalid numbers
Ensure you send messages to valid phone numbers with the right country prefix (e.g., “1” for the United States) to improve SMS and MMS deliverability.
Avoid sending messages to landlines or wrong/disconnected numbers. Be wary of carrier filters that may prevent A2P communications from being sent.
Use sophisticated A2P routing and avoid terms that can trigger filtering.
Routing factors
Check for issues with SMS routing, and use providers with reliable routing services.
“Long Code” text messaging
If you’re sending a high volume of messages, consider using short-code SMS services for better deliverability.
Network congestion
Keep network congestion in mind during peak hours and schedule messages for periods when network traffic is lower. Consider signal strength and connection, and, if required, modify your location to ensure reliable message delivery.
Blocked numbers
Ensure you haven’t been blocked by the recipient, and maintain open and honest communication with them.
DND (Do Not Disturb) Mode
Be mindful of the recipient’s Do Not Disturb settings and set up other contact or communication times.
Software glitches
To reduce the likelihood of having technical difficulties, keep your software and apps up to date.
Message center number misconfiguration
Double-check that the correct Message Center Number (MCN) is configured on your device.
Message length and format
To guarantee reliable transmission, stick to character limitations, such as the typical 160 characters for SMS messages. For longer messages, use concatenation and other alternative approaches.
Roaming restrictions
Be aware of roaming restrictions when traveling abroad, and consider using alternative messaging platforms.
Sender’s service outage
Stay informed about service outages from your mobile service provider and consider alternative communication methods during outages.
Sender error
Double-check recipient numbers and prepaid plan balances to avoid unnecessary delivery failures.
Carrier blocklists
Be aware of carrier blocklists and engage with carrier support services if needed.
Phone memory issues
Manage your message inbox and consider cloud-based storage to optimize device storage capacity.
Blacklisted devices
Ensure responsible use of mobile devices to avoid blacklisting.
What Is An SMS Delivery Report?
A message delivery report, also called a “delivery receipt,” is a message you receive from your SMS server, known as the SMSC (Short Message Service Centre), confirming that the SMS message you sent has been delivered to the recipient’s phone.
1. User sends an SMS
The user composes and sends an SMS message from their phone.
2. Message to SMSC
The SMS is sent to the Short Message Service Center (SMSC), which acts as an intermediary for SMS messages.
3. Temporary Storage at SMSC
The SMSC temporarily stores the SMS while it processes the message and attempts to deliver it.
4. Delivery Attempt
The SMSC attempts to deliver the SMS to the recipient’s phone number.
5. Check for Network Coverage
If the recipient’s phone has poor network coverage or is turned off, the delivery may fail at this stage.
6. Confirmation Message
If the message is successfully delivered to the recipient’s phone, the recipient’s phone sends a confirmation message back to the SMSC.
7. Generation of Delivery Report
If requested, the SMSC generates a delivery report and attempts to transmit it to the user.
8. Custom Delivery Reports
Some SMSCs can send a receipt to the user if the message starts with “*0#,” indicating a request for delivery reports.
9. Delivery Report Details
The delivery report provides detailed information about the status of all messages sent to the supplier (or carrier). This includes information about message filtering, delivery status (e.g., “hard bounce” or “soft bounce”), and whether the message was successfully delivered to the recipient’s device.
Conclusion
Ever sent a text and wondered if it got through? A delivery report in a bulk SMS solution tells you that your message was successfully delivered. It gives you peace of mind, and if there’s an issue, it alerts you so you can take action.
For businesses sending bulk messages, delivery reports are essential for tracking the success of your SMS campaigns and helping you make necessary adjustments.
TextGrid, a leading API solution provider, makes it easy for you to access the latest features in SMS wholesale software so you can manage your SMS wholesale business more efficiently.



![Telnyx Alternatives: The Complete List [2024]](https://textgrid.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Banner_12.png)